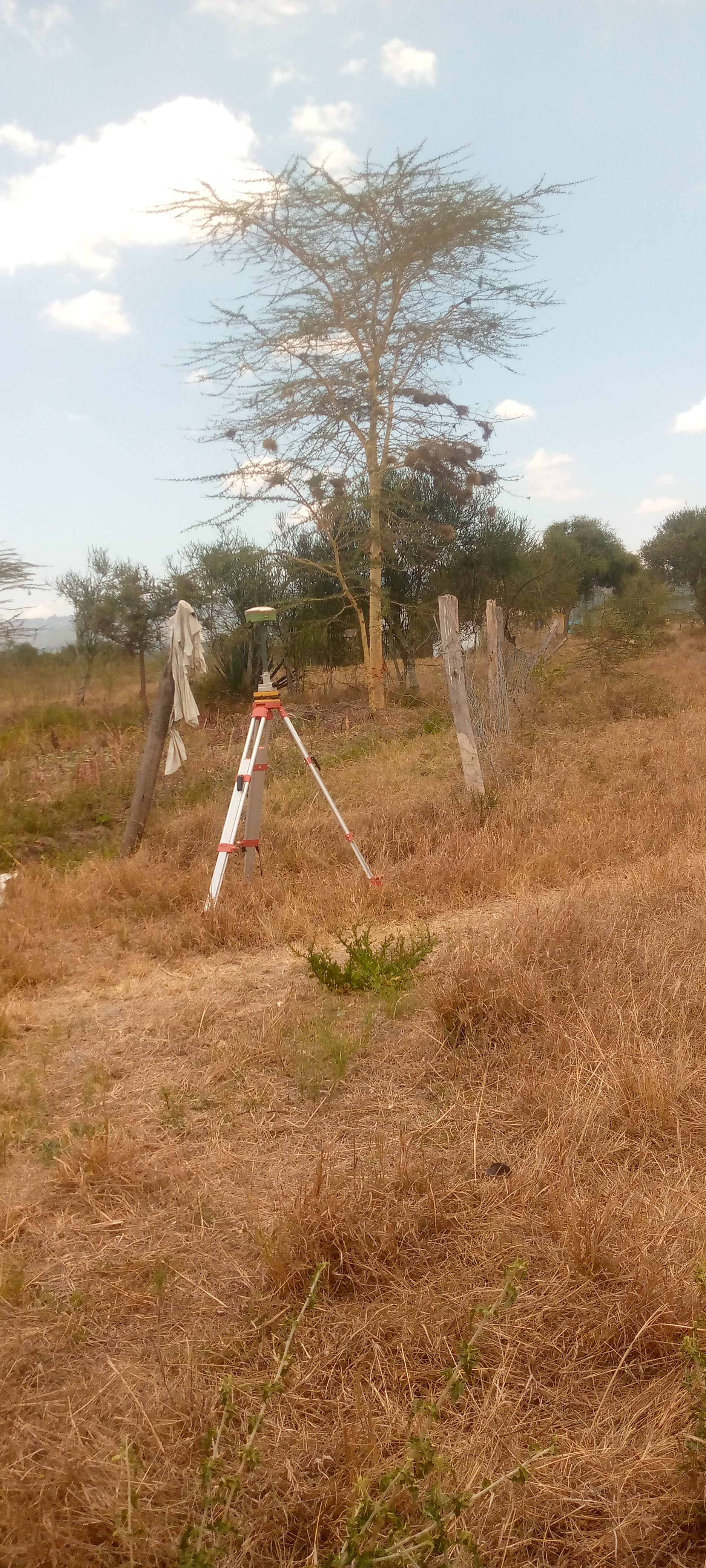
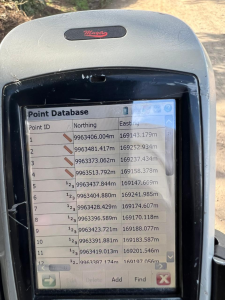
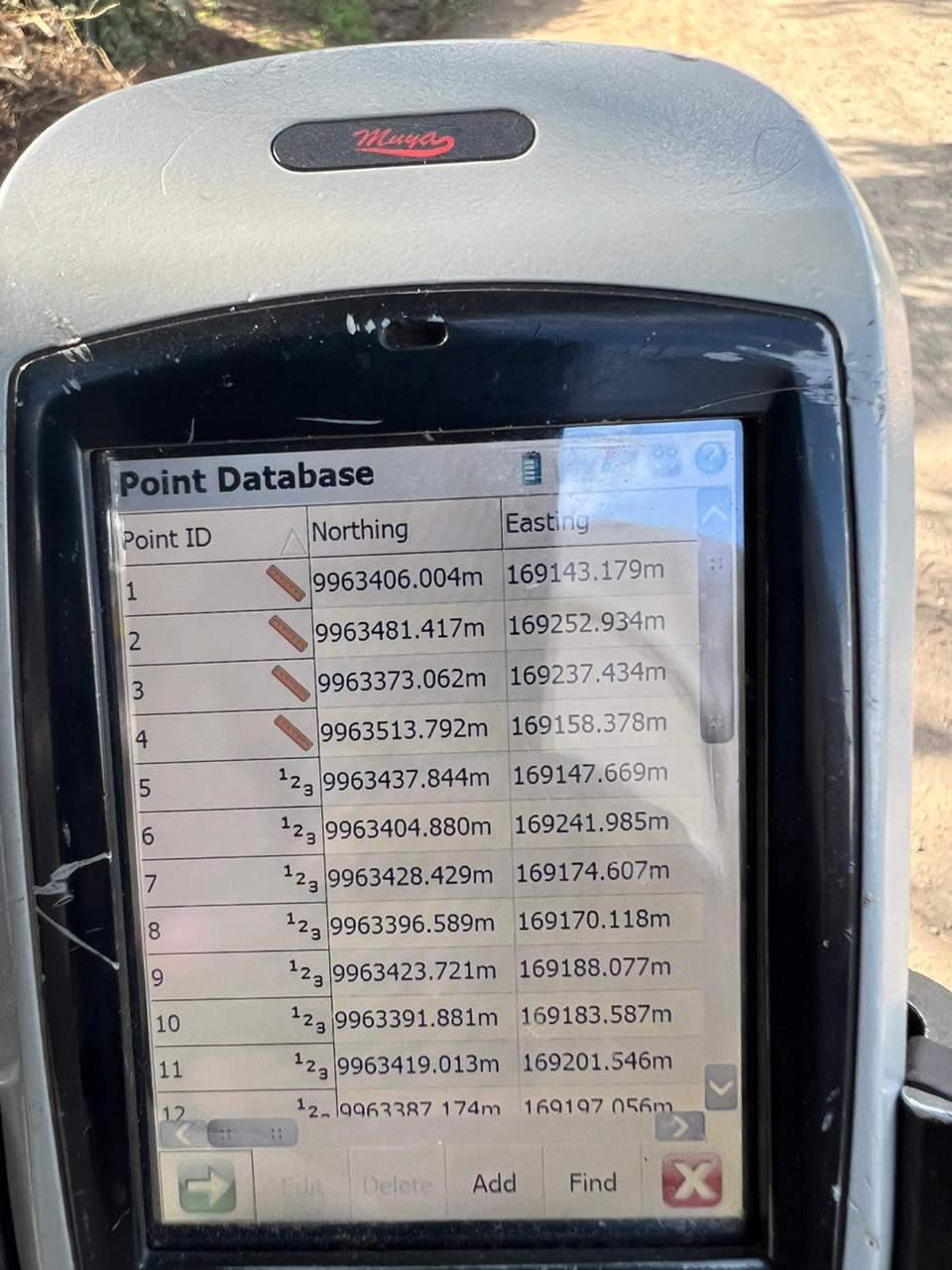
Land law is a branch of law that governs the rights, interests, and responsibilities related to land and real property. It defines how land is owned, used, transferred, leased, or inherited. Land law is fundamental in regulating relationships between individuals, the community, and the state concerning land ownership and use.
Land law covers a wide range of legal principles and topics, including:
Ownership rights (who can own land and under what conditions)
Tenure systems (freehold, leasehold, customary tenure, etc.)
Land registration (recording of land titles and transactions)
Transfers and conveyancing (sale, gift, inheritance, or mortgage of land)
Leases and tenancies (landlord-tenant relationships)
Easements and encumbrances (rights of way, utility access, etc.)
Zoning and land use (regulations on how land can be used)
One of the key objectives of land law is to ensure legal certainty and protect property rights, while also balancing public interest, such as environmental protection, urban planning, and social justice.
In many countries, land law consists of a mix of:
Statutory law (laws enacted by the government)
Common law or case law (judicial decisions)
Customary law (traditional practices, especially in rural or indigenous communities)
Land law also plays a crucial role in:
Resolving disputes over boundaries or ownership
Regulating land development and urban planning
Enabling land reforms and redistribution
Facilitating invest
ment in real estate and infrastructure
- Teacher: Admin User